Some common orthodontic terms and vocabulary.
Appliance
Any device used to change the position of the teeth or jaws or to influence growth.
Archwire
A special U-shaped metallic alloy that is customized to allow proper straightening and movement of the teeth; attaches to orthodontic brackets to guide tooth movement.

Band
A bracket for a molar or back tooth; fits around the entire tooth.
Bonding
The process by which brackets are attched to the teeth by an adhesive.

Bracket
A piece of shaped metal or ceramic that is affixed to each tooth; serves as the “handle” that allows us to grab onto and control the movement of each tooth, individually.
Bruxism
Habitual grinding of the teeth; often occurs while sleeping.
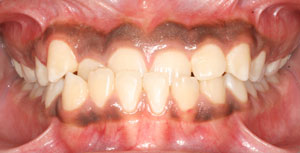
Crossbite (Anterior)
An abnormal relationship of teeth whereby the front teeth in the upper jaw fit inside the front teeth in the lower jaw when during biting.
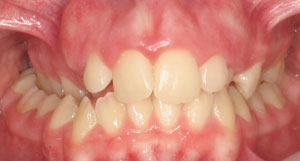
Crossbite (Posterior)
An abnormal relationship of the back teeth whereby the upper teeth fit inside the lower teeth during biting.

Crowding
Dental malalignment caused by inadequate space for the teeth.
Deband
The removal of cemented orthodontic bands.
Debond
The removal of bonded orthodontic brackets.

Deepbite
Excessive vertical overlap (overbite) where the upper front teeth completely or mostly cover the lower front teeth; the lower front teeth may bite into the gums behind the upper front teeth.
Diastema
A space between two adjacent teeth.
Early orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment started while the patient is still in the transitional or primary dentition, before all the permanent teeth have erupted; also called interceptive orthodontic treatment or Phase I treatment. Read more.
Elastics (rubber bands)
Aid in moving teeth in certain directions; usually attach to hooks on the brackets or the archwires.
Extraction
Removal of a tooth.
Fixed Appliance
an orthodontic appliance whose attachments are bonded or cemented to the teeth and cannot be removed by the patient; AKA “braces”.
Frenectomy
The surgical removal or repositioning of the frenum (the attachment of the upper lip to the gums, between the upper front teeth); often done when a diastema (space) was present between the upper front teeth before treatment, in order to enhance the stability of the closure of the diastema.
Functional appliance
Orthodontic appliances, either fixed or removable, which utilize the muscle action of the patient to produce tooth or jaw movement; often used in an attempt to modify the growth of the mandible; Herbst appliance is an example.
Gingiva
The tissue that surrounds the teeth; AKA “gums”.
Habit therapy
Treatment designed to prevent potentially damaging habits, usually involving thumb or finger sucking or tongue thrusting; may also correct an irregularity of the teeth which had been caused by a habit; counseling or appliance therapy (or both) may be utilized for treatment.

Hawley Retainer
A removable retainer used to stabilize teeth in their new positions after orthodontic treatment is complete; consists of acrylic (plastic) that covers the palate on the top jaw and the gums behind the lower teeth on the lower jaw and a metal wire that runs across the upper and lower front teeth; can also perform minor tooth movement with these retainers.

Headgear
A metal bow which fits into upper molar bands, used with a comfortable cloth that fits around the back of the neck. It is used to correct overbites and make smiles more beautiful. It is also worn by popular rock stars in totally awesome music videos.
Herbst appliance
An orthodontic appliance (fixed or removable) that serves to posture the mandible forward, in an attempt to modify the growth of the mandible; a type of functional appliance.
Impacted tooth
The total or partial lack of eruption of a tooth well after the normal age for eruption.
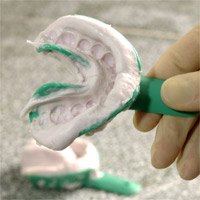
Impression
A negative image of a tooth or dental arch; produced by placing an elastic compound like alginate in a metal or plastic tray and inserting the tray into the mouth around the teeth until the compound stiffens; when the impression is removed from the mouth, it is filled with plaster to produce an exact reproduction of the teeth or dental arch; used for diagnosis of orthodontic problems and for the fabrication of certain appliances.
Interceptive orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment started while the patient is still in the transitional or primary dentition, before all the permanent teeth have erupted; also called early orthodontic treatment or Phase I treatment.
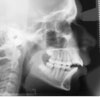
Lateral cephalometric radiograph
An x-ray taken of the side of the face and skull in order to measure relationships of the teeth to the jaws and of the jaws to the skull; used for diagnosis of orthodontic problems.
Lingual holding arch
A fixed orthodontic appliance that consists of a wire running along the tongue-side of the lower teeth and attaches to the lower back teeth (molars); used to maintain space during the transition from the primary teeth to the permanent teeth.
Malocclusion
A deviation from normal when the teeth are in occlusion (biting together).

Mandible
Lower jaw.
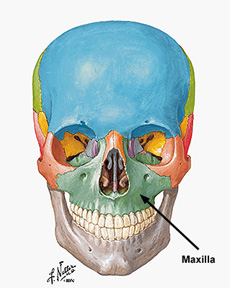
Maxilla
Upper jaw.
Mixed dentition
The developmental stage during which both primary and permanent teeth are present in the mouth; from approximately age 6 to age 12.

Mouthguard
A removable plastic appliance that covers the teeth; worn during contact sports in order to protect the teeth and supporting jaw structures.
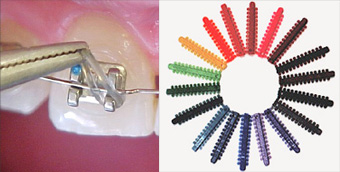
O-ring
A round tie that secures the archwire within the bracket slot. Can be clear or colored.
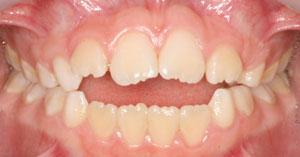
Openbite
A malocclusion in which the upper front teeth do not contact the lower front teeth; can place excessive pressure on the back teeth.

Orthodontist
A dental specialist who has completed an advanced post-doctoral residency of at least two academic years in the area of orthodontics; a specialist in the movement of teeth as well as the growth and development of the teeth and facial structures.
Orthognathic surgery
Surgery performed when a discrepancy in the size and/or position of the jaws occurs; usually accomplished in conjunction with orthodontic therapy; AKA corrective jaw surgery.

Overbite
Vertical overlap of the upper front teeth over the lower front teeth.
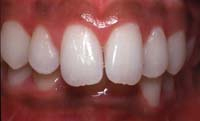
Overjet
Horizontal protrusion of the upper front teeth in front of the lower front teeth.
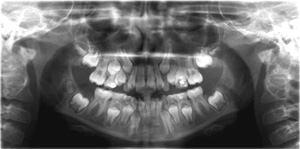
Panaromic radiograph
An x-ray of both the upper and lower jaws, the teeth, and surrounding structures; AKA “pan”; used in the diagnosis of orthodontic problems.
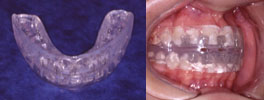
Positioner
A removable elastic orthodontic appliance molded to fit the teeth on a ‘setup’ made by repositioning the teeth from a plaster cast; typically used to achieve fine adjustments and retain corrected positions during the finishing stages of treatment.
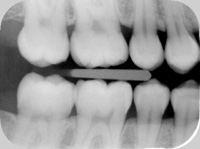
Radiograph
X-ray.
Removable appliance
An orthodontic appliance that is not permanently attached to the teeth and is removable from the mouth; an example is a retainer.

Retainer
An orthodontic appliance that is used to maintain the position of the teeth following orthodontic treatment; can be fixed or removable.
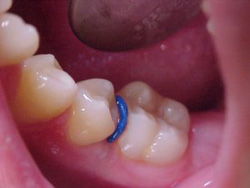
Separator
Small elastics placed between the back teeth that serve to make space for bands between the teeth.
Space maintainer
An appliance that is used when a primary tooth is lost prematurely in order to prevent the closure of the space before the eruption of the permanent successor; also used to maintain leeway space.
Supernumerary tooth
An extra tooth that develops.
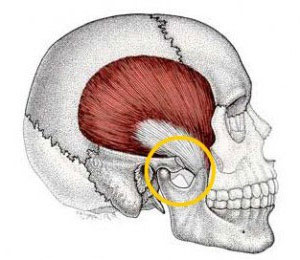
TMJ (temporomandibular joint)
One of the two paired joints between the mandible and the skull; located just in front of the ears.
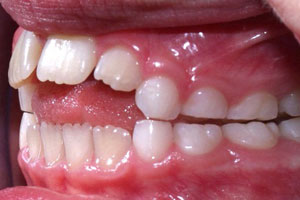
Tongue thrust
Abnormal position of the tongue between the front teeth, especially during swallowing; can produce an openbite.
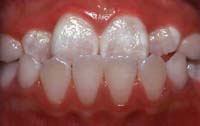
Underbite
Occurs when the lower front teeth are positioned in front of the upper front teeth.




